Dual Inhibition of Xanthine Oxidase and Cyclooxygenase-2 by Aframomum melegueta
In Silico Insights into Multi-Target Therapeutics for Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/iijbs.v3i1.32Keywords:
Inflammation, oxidative stress, xanthine oxidase, cyclooxygenase-2, Aframomum melegueta, molecular dockingAbstract
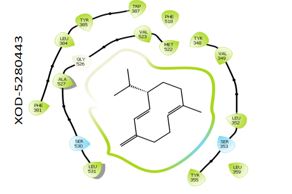
Inflammation and oxidative stress are key drivers of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative conditions. Xanthine oxidase (XOD) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) are critical enzymes in these pathways. However, current therapies targeting these enzymes individually often cause significant side effects. This study investigates the dual inhibitory potential of compounds from Aframomum melegueta on XOD and COX-2 using in silico approaches. A total of 145 compounds were screened using high-throughput virtual screening (HTVS), standard precision (SP), and extra precision (XP) molecular docking. The top four compounds for each enzyme were further analyzed using MM-GBSA and QSAR. For XOD, Apigenin (-9.480 kcal/mol), ϒ-Cadinene (-6.695 kcal/mol), α-Cadinene (-6.535 kcal/mol), and Thymol (-6.184 kcal/mol) emerged as top inhibitors. For COX-2, Germacrene D (-7.848 kcal/mol), Muurolene (-7.664 kcal/mol), α-Cadinene (-7.619 kcal/mol), and Valencene (-7.552 kcal/mol) were identified. Machine learning predicted pIC50 values of 6.153–6.331 for XOD inhibitors and 6.113–7.106 for COX-2 inhibitors. Pharmacokinetic profiling revealed favorable drug-like properties for all compounds. Notably, α-Cadinene demonstrated dual inhibition of both enzymes, highlighting its potential as a multi-target therapeutic agent. These findings suggest A. melegueta compounds as promising candidates for managing inflammation and oxidative stress-driven diseases, warranting further in vivo validation and optimization.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Olukayode Olusola Odubela, Afees John Olanrewaju

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
