Effects of Four Local Species of Beans Consumed in South-eastern Nigeria on Selected Biochemical Indices of Wistar Albino Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/iijbs.v1i1.1Keywords:
Phaseolus vulgaris, Cajanus Cajan, Red kidney bean, Liver marker enzymes, Kidney function, Black turtle beanAbstract
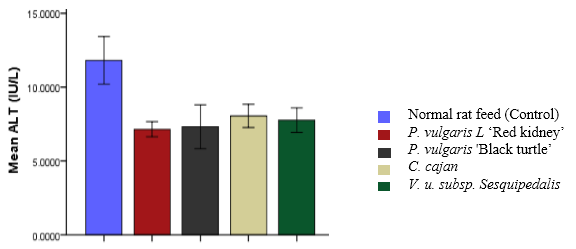
The chemical composition and the effects of four local species of beans on the liver and kidney function of Wistar albino rats were examined. The four beans species are Cajanus Cajan, Vigna unguiculata subsp. sesquipedalis, Phaseolus vulgaris L ‘Red kidney’, and Phaseolus vulgaris 'Black turtle’. The results obtained for the proximate composition analysis revealed that the protein content of the bean species was higher in P. vulgaris L ‘Red kidney’ (18.54±0.01a %), and P. vulgaris 'Black turtle’ (18.36±0.01a %) with no significant difference at P< 0.05. The phytochemical composition analysis revealed that the beans contain various phytochemicals including some anti-nutritional factors. The mineral composition analysis shows that V. u. subsp. Sesquipedalis had a higher level of minerals (4.80±4.43a mg/100g) followed by C. cajan (3.24±2.64b mg/100g). The experimental design comprises of 30 male Wistar albino rats distributed into 5 groups of 6 rats each. Each group except the control received 50g of normal rat feed + 100g of beans body weight. The effects of the beans species on the biochemical parameters suggest no adverse effects when compared to the control. Despite that, these beans contain high nutritional components that are of nutritional interest as as well as some anti-nutritional factors.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Ifemeje et al.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
