Eating Habits and Nutritional Status of Adolescents and Young Adults in Tertiary Institutions in Port Harcourt Metropolis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/ijph.v4i1.23Keywords:
Eating habits, nutritional status, adolescents, young adults, studentsAbstract
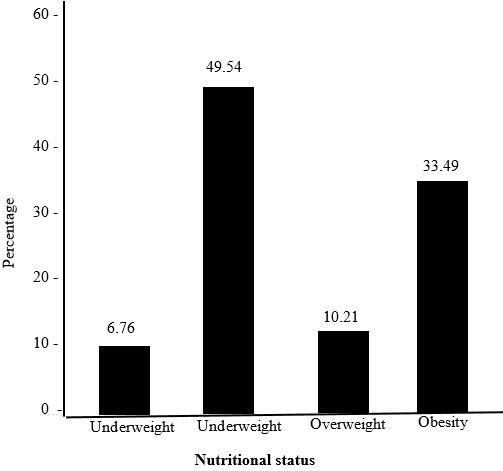
University students tend to have poor eating practices which are related to nutritional status. The objective of this study was to assess the eating habits and nutritional status of adolescents and young adults in tertiary institutions in Port Harcourt metropolis. The study adopted a cross-sectional descriptive design. The population consisted of adolescents and young adults in tertiary institutions in Port Harcourt aged 17-25 years. A multistage sampling technique was used to draw a sample size of 296 respondents from the study. Data were obtained using a three-part questionnaire (socio-demographic profile, eating habits, and anthropometric parameters). The data were statistically analyzed using frequency and percentage and findings were presented on charts and tables. Females constituted 64.86% of respondents with about 83.78% of the respondents within the ages of 21-25. Most students (78.38%) reported taking one meal a day with breakfast being the most skipped meal. Most students (56.76%) eat in the cafeteria and 72.97% ate late. Snacking was common among these students as 75.67% admitted consuming snacks 1-3 times, 3-5 times or more than 5 times weekly. Weekly intake of fish and meat, and fruits and vegetables were high (83.49% and 81.09% respectively). Among the respondents, 20(6.76%) were underweight and 99(33.49%) were obese. About half (147) of the respondents (49.54%) had normal weight while 30(10.21%) were overweight. Frequency of consumption, fruit and vegetable consumption, meat and fish intake, fast food consumption, and breakfast skipping were related to nutritional status. Overall, the results revealed that the majority of the students had poor eating habits. This suggests the need to increase nutritional counselling on healthy eating habits in universities and to take appropriate interventions to improve nutritional status among university students.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 G. A. Amadi, M. A. H. China

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
