Study on Multidrug, Extensive Drug and Pan Drug Resistance in Septicemic Infants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/ijamb.v2i1.12Keywords:
Septicemic Infants, Multi Drug Resistant, Extensive Drug Resistant, Pan Drug ResistantAbstract
Background: Septicemia is common in neonates and is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the early stages of life. With positive signs and symptoms, early-stage diagnosis and treatment of neonates are important to decrease death rates and complications. This article will provide an in-depth study to evaluate the resistance pattern including multi, extensive and pan drugs resistance in septicemic infants.
Materials and Method: A descriptive cross-sectional study was carried out at Rehman Medical Institute (RMI), Hayatabad Medical Hospital (HMC) and Khyber Teaching Hospital (KTH), Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) and 999 blood samples were collected from septicemic infants (1 day to 1 year of age) belonging to both genders. Blood was screened for the presence of pathogenic bacteria and their complete data was collected and analyzed with SPSS-20.
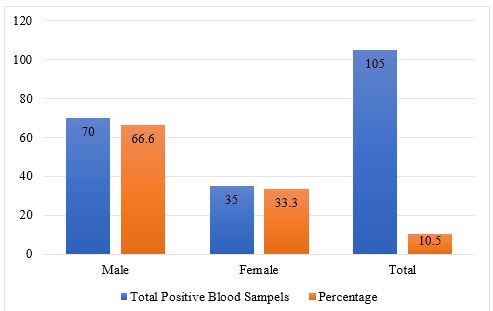
Results: In total 999 collected blood samples, 105 (10.5%) were found positive for septicemia. In these 105 positive cases, males were 70 (66.6%) while 35 (33.3%) were female infants. Out of 105 positive cases, 66 (62.8%) revealed growth of Gram positive while 39 (37.1%) for Gram negative bacteria. The most common Gram positive bacterial isolates were Staphylococcus aureus 56 (53.3%) and Enterococcus spp 10 (9.5%) while Gram negative were Klebsiella pneumonia 11 (10.5%) followed by Escherichia coli 10 (9.5%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa 7(6.7%), Acinetobacter baumannii 5 (4.8%), Stenotrophomonas mettophilia 3 (2.9%) and Enterobacter, Serratia and Citrobacter spp (one isolate each).
Conclusion: The S. aureus isolates were resistant to Penicillin and Cephalosporin while were sensitive to Glycopeptides and Oxazolidinone group. The Enterococcus isolates were resistant to Aminoglycoside and Macrolides group while were sensitive to Glycopeptides, Rifamycin and Oxazolidinone. The isolates of Enterobacteriaceae were mostly resistant to penicillins and were sensitive to colistin and Piperacillin/ Tazobactam. In the current study 63.8% isolates were MDR, 2.9% XDR and luckily no PDR isolate was found.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Muhammad Riaz, Ibrar khan, Shahtaj Khan, Fazal Sattar, Muhammad Ilyas khan, Sadiq Azam

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
