Moisture Sorption Characteristics of Lafun Flour
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/iajnfms.v2i1.60Keywords:
Sorption, Packaging materials, Equilibrium Moisture Content, Water activity, ModelsAbstract
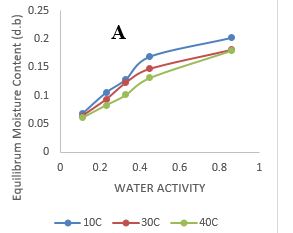
Understanding the relationship between relative humidity and equilibrium moisture content (EMC) of any food material assist in maintaining good keeping quality. The adsorption isotherms for lafun supplemented with soy cord and residue were investigated. Six saturated salts were used which are Lithium chloride (RH: 11% aw, 0.22); potassium (RH: 93%, aw: 0.38); Magnesium chloride (RH: 33%, aw0.56); Potassium chloride (RH: 86%, aw: 0.40); Potassium acetate (RH: 23%, aw: 2.81); Potassium carbonate (RH: 43%, aw: 1.15) providing constant relative humidity environments ranging from 11 – 93%. The experimental data were compared with five widely recommended models in the literature for food adsorption isotherms (GAB, Oswin, Modified Oswin, BET and Henderson). The moisture adsorption isotherm were sigmoidal in shape and was influenced by temperature. Oswin model was best fits for all the samples at different temperatures. The monolayer moisture values for BET model of commercial ‘lafun’ sample are 0.040, 0.036 and 0.034 kgkg-1, ‘lafun’ enriched with curd 0.036, 0.038 and 0.031 kgkg-1, control ‘lafun’ 0.057, 0.038 and 0.025 kgkg-1, and ‘lafun’ enriched with residue 0.030, 0.036, 0.029 kgkg-1 at 10, 30 and 40ºC respectively while GAB model gave monolayer moisture values of 0.0682, 0.063 and 0.053 kgkg-1 for commercial ‘lafun’ sample, 0.045, 0.042 and 0.039 kgkg-1for ‘lafun’enriched with curd, 0.065, 0.042, 0.039 kgkg-1for ‘lafun’ commercial sample 0.081, 0.066 and 0.061 kgkg-1for ‘lafun’ enriched with residue at 10 ºC, 30ºC and 40 ºC respectively
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Uche Capulet Anyaiwe, Kennedy Ahamefula Okoronkwo, Taiwo Ayodele Aderinola

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
