Amino Acid Profile, Mineral Composition, In Vitro Protein and In Vitro Starch Digestibility of Enriched Gari Samples
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/ijnfs.v3i3.61Keywords:
soy residue, soy curd, gari, amino acid, protein digestibility, starch digestibilityAbstract
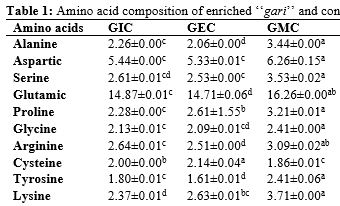
Amino acids, which act as significant macromolecules for the regulation of critical metabolic pathways, are provided by protein crops (such as soybeans), which are crucial for human nutrition. This study aimed to examine and compare the amino acid profile, mineral composition, and in-vitro protein and starch digestibility of gari enriched with soy curd and soy residue at a 10% substitution level. The amino acid profile results showed a significant increase (p<0.05) in both essential and non-essential amino acids in soy-enriched gari compared to the control sample. Specifically, gari enriched with soy residue (GMR) and gari enriched with soy curd (GMC) had 29.02 and 32.5%, respectively compared to 24.14 for the control sample (GIC). For the non-essential amino acids, GIC, GMR and GMC had 33.39, 33.35 and 39.38%, respectively. The enriched samples had higher mineral contents compared to the control gari. During enrichment, the enriched gari's in vitro protein digestibility rose whereas its in vitro starch digestibility declined (p<0.05) sharply. These findings suggest that soy curd or residue can significantly enhance the nutritional quality of gari, particularly by improving its amino acid profile and protein digestibility, though with a trade-off in starch digestibility.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Uche Capulet Anyaiwe, Taiwo Ayodele Aderinola

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
