Antibacterial Effects of Piliostigma thonningii and Anacardium occidentale against Some Food Spoilage Pathogens
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/ijnfs.v3i3.63Keywords:
food safety, food preservatives, Anacardium occidentale, Piliostigma thonningiiAbstract
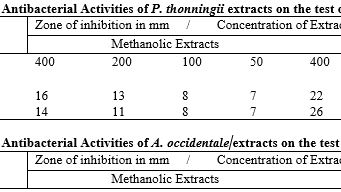
This study investigated the antibacterial activities of Piliostigma thonningii and Anacardium occidentale against food spoilage bacteria, specifically Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Additionally, the phytochemical contents of these plants were analyzed. Bacterial isolates were obtained from the Microbiology Laboratory at Federal University Birnin Kebbi and re-identified through various biochemical tests. Leaf samples of both plants were collected from the university premises, authenticated by the Botany Unit of the Department of Biological Sciences, and then subjected to drying and extraction. The antibacterial activities of the plant extracts were determined using the agar well diffusion method. Biochemical tests confirmed the identities of E. coli and S. aureus as the test bacteria. Phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of tannins, terpenoids, flavonoids, steroids, alkaloids, cardiac glycosides, glycosides, saponins, and volatile oils in the plant extracts. The antibacterial activity results indicated inhibition zones of 14 mm for methanolic extracts and 26 mm for aqueous extracts of P. thonningii against E. coli. Similarly, P. thonningii showed inhibition zones of 16 mm for methanolic extracts and 22 mm for aqueous extracts against S. aureus. For A. occidentale, inhibition zones of 18 mm for methanolic extracts and 25 mm for aqueous extracts were observed against E. coli, while zones of 20 mm for methanolic extracts and 26 mm for aqueous extracts were recorded against S. aureus. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for P. thonningii against E. coli were 50 mg/ml for methanolic extracts and 25 mg/ml for aqueous extracts. For S. aureus, the MIC values were similarly 50 mg/ml for methanolic extracts and 25 mg/ml for aqueous extracts. For A. occidentale, the MIC values against E. coli were 100 mg/ml for both methanolic and aqueous extracts, while against S. aureus, the values were 50 mg/ml for methanolic extracts and 25 mg/ml for aqueous extracts. The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) values for P. thonningii against E. coli were 1000 mg/ml for methanolic extracts and 50 mg/ml for aqueous extracts, while against S. aureus, the MBC values were 100 mg/ml for methanolic extracts and 50 mg/ml for aqueous extracts. For A. occidentale, the MBC values against E. coli were 200 mg/ml for both methanolic and aqueous extracts, and for S. aureus, the MBC values were 100 mg/ml for methanolic extracts and 50 mg/ml for aqueous extracts. In conclusion, both P. thonningii and A. occidentale demonstrated potential as sources of antibacterial agents against common food spoilage bacteria.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Jonathan Bawa Maganda, Sani Jafar, D. R. Jabaka, V. E. Ukatu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
