Investigation into Proximate, Phytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Functions of Active Agent Saponin Extracted from Momordica charantia (A Local Herbal Leaf)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/ijnfs.v4i1.73Keywords:
Saponin, Phytotocicity, Antimicrobial, Momordica charantia, ProximateAbstract
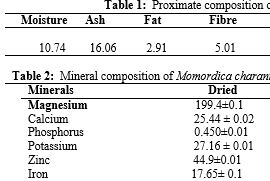
Momordica charantia is a medicinal bitter leaf, which has been in use for ages by our fore fathers, hence the need to investigate its biological activities in order to elucidate its medicinal values. The proximate and mineral compositions of M. charantia were determined and its protein, fibre, phosphorus, calcium, potassium, sodium, manganese, iron, copper and zinc contents were 25.09, 5.01, 0.45, 1.04, 2.72, 72.6, 1.99, 1.77, 70.7 and 44.9 mg/100 g, respectively. The result further showed that the sodium content in the M. charantia is higher than all other elements present, hence helping in the maintenance of acid-base balance in the body. The phytotoxic assay of saponin extracted from M. charantia on maize seedlings was concentration-dependent and showed an inhibitory effect on growth of root and shoot of the maize seedlings. The phytochemical assay of the sample showed that M. charantia contained saponin (80.32%), phytic acid (60.40%), tannin (24.10%) and cyanide (15.5%), respectively. The antimicrobial activities of the saponin extracted from M. charantia was observed to have an inhibitory effect on the microbial growth such as; E. coli, Streptococcus pyrogens, Klebsiella and Enterobacter. The study, therefore, concluded that M. charantia is fully enriched with saponin levels that could be exploited for as functional food and antimicrobial agent in the areas of food and health applications
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ayorinde D. Olowookere, Olamide O. Ojo, Sunday A. Malomo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
