Kidney Bean Protein Products: The Alternative Non-Pharmacological Potential Agents in the Management of Hypertension in Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/ijnfs.v4i1.76Keywords:
kidney bean, albumin, globulin, hydrolysates, non-pharmacological, hypertensionAbstract
Hypertension, a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated (systolic and diastolic values of ≥140 mmHg and ≥90 mmHg, respectively), is characterized by insufficient relaxation of blood vessels and reduced blood flow. Kidney bean protein (KBP) albumin (KBPA) and globulin (KBPG) were produced by salt extraction method while the isolate (KBPI) was prepared by alkaline extraction followed by isoelectric precipitation. Enzymatic hydrolysates of KBPI were prepared by treatment with alcalase (KBPH-A) and pepsin+pancreatin (KBPH-PP), respectively. The in vivo antihypertensive activities and management of endogenous biochemicals of KBP products in the induced-hypertensive rats were evaluated after determining their amino acid (AA) profile. The AA profile showed that hydrophobic amino acid (HAA) of KBPG (41%) is higher than KBPA (39%) and KBPI (36%), respectively but with similar (11%) aromatic amino acids (AAA). The enzymatic hydrolysis process resulted in increased contents of HAA and AAA of KBPH-A and KBPH-PP (42-45%; 14%), respectively. The hydrolyzed proteins had significantly (p<0.05) higher in vivo antihypertensive activities (72 and 81%) than the non-hydrolyzed (20 and 25%) KBP in the induced-hypertensive rats, which suggested the role of hydrophobicity, strong disulfide bonds and hydrolysis during inhibition. The KBPH-PP had the lowest values for ALP (14 U/I), AST (19 U/I) and ALT (18 U/I) which signified the highest management of liver biochemicals levels in the induced-hypertensive rats among the protein fractions. This study importantly showcased the production of potential compounds (protein hydrolysates) from kidney bean proteins in the management of high blood pressure.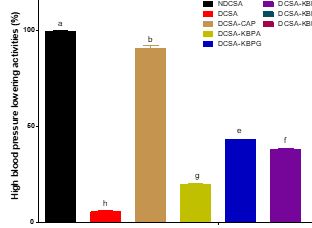
Downloads
Published
2025-02-14
How to Cite
Udeh, C. C., Idolo, I., Akpodiete, J., & Malomo, S. A. (2025). Kidney Bean Protein Products: The Alternative Non-Pharmacological Potential Agents in the Management of Hypertension in Rats. IPS Journal of Nutrition and Food Science, 4(1), 324–331. https://doi.org/10.54117/ijnfs.v4i1.76
Issue
Section
Articles
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Charles Chiedu Udeh, Sunday Abiodun Malomo, Ifie Idolo, Job Akpodiete

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
