Amino Acid Profiles of Avocado (Persea americana Mill) Leaf products enhanced their Antioxidant and Anti-diabetic Activities
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54117/ijnfs.v4i1.78Keywords:
Avocado leaf, Persea americana, nutritional composition, amino acid, phytochemicals, antioxidants, functional foodAbstract
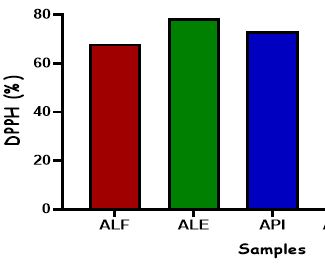
This study investigated the effect of different extraction processes on the therapeutic properties of avocado leaf extracts by subjecting the extracts to the amino acid compositions, antioxidants and carbohydrates inhibition analyses. Samples obtained from this study were Avocado leaves flour (ALF), Avocado leaves aqueous extract (ALE), Avocado leaves protein isolate (API), Avocado leaves pancreatin-protein hydrolysates (APHPAN) and Avocado leaves lactic acid bacteria-protein hydrolysates(APHLAB), respectively. The APHPAN and APHLAB were predominantly composed of glutamine (8.06-8.08%) and valine (6.98-7.00%) when compared to other samples. The samples ALE and APHLAB exhibited good antioxidant properties indicated by its strong ability to scavenge ABTS, FRAP, DPPH radicals and reduced Fe3+ to Fe2+.They also significantly (p<0.05) inhibited α-amylase (40-80%), α-glucosidase (25-58%) and pancreatic lipase (28-40%) enzymes, respectively. Hence, the outcomes from this finding suggested the avocado leaves to be a valuable source for functional food in the management and prevention of some degenerative diseases.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Precious Adesola Ayodeji, Sunday Abiodun Malomo, Oluwole Steve Ijarotimi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
